Reactor cooling Down
SAKNAFTA Egypt Accelerated reactor cooling….
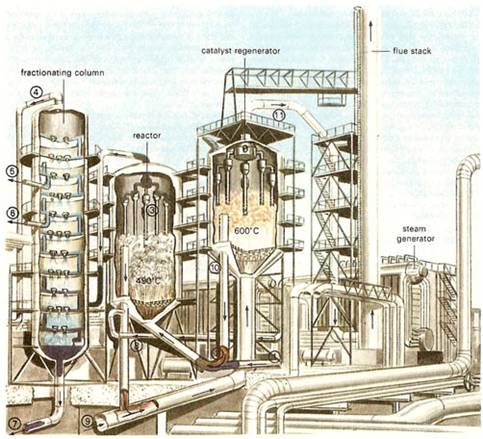
The hydrocarbon Processing Industry employs a complex group of processes to reduce crude to usable end products. Historically, many of these processes have utilized catalysts to improve effectiveness and efficiency. The use of catalysts increases the more the quality of crude decreases. This increase in the use of catalysts has lent more attention to catalyst turnaround, handling and the time associated with these activities.
Enhanced Nitrogen Reactor Cool-downs are executed to speed up the reactor cool-down process.
The method delivers:
* Fast cool-down to minimize downtime
* Lower cost over conventional methods
*Safe, controlled operation
* Lower reactor entry temperatures for safer, faster work
*Optimized cool-downs through advance planning
The catalysts in such processes are contained in large reactors. During operation, the effectiveness of the catalyst is reduced. This reduction is primarily due to coke formation. Eventually, the catalyst must be removed and replaced with a fresh one. For the removal of the catalyst, the reactor must first be cooled from the operating temperature of 260 – 485 ºC to less than 38 ºC. The cool-down of the reactor is a time consuming procedure, often requiring three to four days. This time can be reduced by several days using Enhanced Nitrogen Reactor Cool-downs at a fraction of the cost of conventional methods.